Mobile Phone Technology
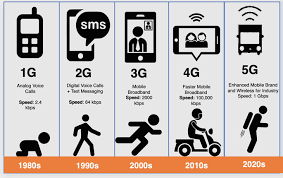
Generations of the Mobile Phone.
image ©researchgate0G Phones The cellular concept is the basis of modern mobile phones. Prior to this, there were many radio telephones that used PTT (push-to-talk) technology. As this technology used the entire available spectrum to connect one phone, it was unable to scale to the level needed for modern mobile phone users. Therefore, a different model for mobile phone networks was required.
1G Phones The first mobile phones used analogue technology. These phones were based on circuit switching and still used dedicated frequencies, so there was still a capacity issue. The cellular concept enables many cells to share the same frequencies. As these cells are small, a larger overall phone capacity is possible. These phones' only function was to make phone calls, and the ability to move around while speaking was novel. Phones of this generation were large and heavy, mainly due to the size of the battery.
2G Phones The switch to digital technology enabled digital communications with greater frequency sharing and capacity. These phones also offered SMS messaging and slow internet access. Typical phones of this era include the Nokia 7110, the first phone to provide internet access. Initially, Internet access was via a dial-up connection, but later, with the introduction of GPRS technology, a more modern way of accessing the Internet became available. Later, EDGE technology further improved network speeds.
3G Phones The search for faster data speeds began with the introduction of 3G mobile phone technology. The demand for internet-based services led to a demand for greater network capacity and speed. Basic 3G networks were based on UMTS technology, operating at 800 MHz and 2.1 GHz. This increased capacity enabled video streaming and even 3GTV trials. Typical phones of this era included the Nokia N95 range. A later development for the 3G network was the HSPA+ software upgrade, which increased speeds.
4G Phones These phones represent a new network driven by the need for speed and capacity. It is a fully data-based model, showing the focus on data and the internet. The technology used is LTE (Long Term Evolution), which allows for incremental development. Messaging and phone calls are proposed to be implemented via data-driven apps, such as internet messaging and VOIP phone calls. A recent development of 4G is LTE Advanced, also known as 4G+.
5G Phones The initial implementations of the 5G network are an evolution of 4G, providing more speed and capacity through various technical enhancements. The 5G evolution simplifies the core network, bringing many functions to the periphery and the cloud. Massive MIMO provides the extra speed. The initial 5G installation was 5G-NR, which improved the radio (wireless) aspect while using the same 4G core network. Later, mobile operators will move to 5G-SA, which runs on a new 5G core network and offers more advantages to 5G. In the UK, 5G will later see the introduction of mmWaves (26 MHz or 40 MHz). While these are not ideally suited to standard phone applications, they will be useful for adding speed and capacity to the mobile network system.
deepl.com [AI] has been used to improve the text in this description
© mobilephonetechnology.co.uk all rights reserved 2017-2026
