Mobile Phone Technology
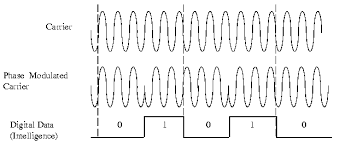
The basis of phase modulation is that changes are made to the phase of the carrier wave and these changes represent 0 or 1. Simple phase modulation (BPSK) shifts the phase 180deg. This simple modulation scheme means 1 bit is sent per carrier wavelength. Hence the maximum data rate is equal to the frequency. So the maximum that a 700MHz wave can transmit is 700 million bits. More complex techniques are used to deliver faster data rates. Various techniques allow for up to 16 data values to be sent per carrier wavelength. Phase modulation is available in an analogue or digital environment, mobile phone communications are digital. In the mobile communications context the methods are called PSK (Phase Shift Key). The "Key" implying that the different changes to the phase represent a key or binary value.
In any form of PSK there are different states used to define different data values. The most basic form BPSK uses phase changes of 180deg to indicate 0 or 1. One issue is that the receiver will have a different clock to the transmitter and at a distance, so receiver needs to find the state changes. One way to make this easier is to use change, no change representing 0 and 1 representing a change in the wave.
BPSK Binary PSK - changes of 180deg making 1 bit data transmitted per change. 0, 1
QPSK Quadrature PSK - changes of 90deg making 2 bits data transmitted per change. 00, 01, 10, 11
8-PSK 8 valued PSK - changes of 45deg making 3 bits data transmitted per change. 000, 001, .. 110, 111
16-PSK is also available with phase changes of 22.5deg. This is much harder to detect. 32-PSK will require 11.25deg changes in phase. This is really difficult to detect and further developments are likely to be impossible. The issue is a balance between the number of bits transmitted with the phase change and the ability to receive the data.
Minimum Shift Key (MSK) - there is an issue with "sharp" changes in a wave caused by the phase changes. These "sharp" changes makes for sideband interference, so whilst one channel may be fast, adjoining channels will have high levels of interference. MSK aims to smooth out these "sharp" changes.
Gaussian MSK is a specific method of MSK. Electronics of a Gaussian filter will reduce the sideband issue. These signals can be amplified in a non-linear amplifier which does not distort the waves and is low on power; good for mobile phone handsets.
© mobilephonetechnology.co.uk all rights reserved 2017-2026
