Mobile Phone Technology
network slicing in 5G
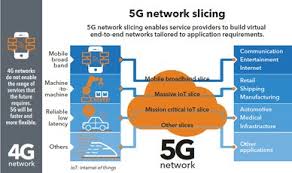
image ©telecomabc.comIn a 4G network each operator will run a general purpose network supporting the range of use, from browsing the Internet, Vo-LTE phone services, streaming and more recently IoT. But many of these applications have different demands on a network Maybe they require very low latency, have a high download data demand, or support many millions of low data devices.
Network slicing is the 5G technology that allows the network to be split into different virtual networks, slices, that provide an end to end virtual network. Each of which can be tailored to the needs of the applications. It is envisaged that some companies would be able to "purchase" their own 5G network and tailor it to their need, in particular in smart factories.
- For example:
- Autonomous vehicles require low latency but not a large amount of data
- Mobile Broadband, more download than upload.
- Massive IoT network lots of little pieces of data.
- Smart factory network to control machines.
- Streaming movie service with a large downstream data demand and no real upstream data demand
- Online Video Games
- General purpose mobile phone network
The network operator could run these different networks themselves, with different revenue models, but also sell virtual networks. Netflix, or similar, may be interested in a streaming virtual network which could be the future of TV. Ford (or another car maker) may wish a virtual network for their autonomous cars. Large scale automated factories could be interested in their own virtual network. Some of these virtual networks will be built on mmWave frequencies, and some on the more general 700Mhz or 3.4GHz frequencies.
Network slicing is seen as a major discriminator that makes 5G much more than an upgrade to 4G, whereas 4G was really a faster and better 3G
© mobilephonetechnology.co.uk all rights reserved 2017-2026
