
 image ©a10networks.com
image ©a10networks.com
When your phone is connected to the mobile network it needs an IP address so that your phone can be found.There are two versions of IP addresses available today IPv4 and IPv6. Whilst we are slowly moving to IPv6 networks many, including the mobile phone networks, are IPv4 networks. If you request the IP address for your phone (whatismyipaddress.com) you will be shown two addresses IPv4 and IPv6. The IPv6 address is more complex, 32 hexadecimal numbers, and will be unique to your device. But the IPv4 address is only 4 hexadecimal number and we have insufficient to go around. Your IPv4 address will be shared with other phones on the network. So how can the mobile network work out which of the phones made a request when the address is not unique but shared
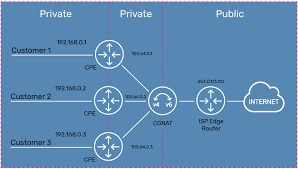
All devices on a home router will also have the same IPv4 address but different IPv6 addresses [if one is shown]. The IPv4 address, something like 85.25.255.191, will be allocated to the router and this router allocates a local address something like 192.168.1.154, to any connected device. As HTTP - the Internet Protocol - is a request / response, the router knows which device (local address) has made the request and can 'route' the responce to the correct address. This is called NAT - Network Address Translation
Why is this important to mobile phone technology? Because this is exactly how IP addresses are allocated to a mobile phone on a mobile network. The IPv4 address allocated to your phone will be shared between a number of mobile phones with the network operator (Vodafone, O2, EE or THREE) using routing software, similar to that used in the home, to allocate the responses to the correct phone. This is CGNAT - Carrier Grade Network Address Translation
CGNAT works well for mobile phones because all requests start from the phone and the network knows where the request has come from and where the response goes to. This also works for mobile broadband when the devices connected initiate the Internet requests, just as occurs on the phone. But some specific services such as hosting a web server, or a camera-stream cannot be hosted in an CGNAT environment. This can be solved if the mobile router has a unique IPv4 address, which the network may give you (for a price). This issue for mobile broadband will be relaxed when the networks runs and IPv6 only network.
© mobilephonetechnology.co.uk all rights reserved 2017-2025
