
Mobile Network Operators (UK)
 A Mobile Network Operator (MNO), also known as a Mobile Network Carrier, is a
provider of the infrastructure upon whi. . .goto page
A Mobile Network Operator (MNO), also known as a Mobile Network Carrier, is a
provider of the infrastructure upon whi. . .goto pageEE
 EE is number one mobile network within the UK, regularly coming out on top
in surveys be that high speed (40Mbps), low. . .goto page
EE is number one mobile network within the UK, regularly coming out on top
in surveys be that high speed (40Mbps), low. . .goto pageVM-O2
 O2 is one of the 4 UK mobile phone operators in the UK. It is owned
by Virgin Media, under the VirginMedia-O2 brand. . . .goto page
O2 is one of the 4 UK mobile phone operators in the UK. It is owned
by Virgin Media, under the VirginMedia-O2 brand. . . .goto pageVodafone
 Vodafone has 19.7% share in the UK mobile phone market and is the 3rd largest
of the mobile phone companies. Together. . .goto page
Vodafone has 19.7% share in the UK mobile phone market and is the 3rd largest
of the mobile phone companies. Together. . .goto pageThree
 THREE is the smallest of the UK mobile operators with 12% of the UK
market. They claim a 99.8% population coverage in . . .goto page
THREE is the smallest of the UK mobile operators with 12% of the UK
market. They claim a 99.8% population coverage in . . .goto pageGenerations of Mobile Phone Technology.
 0G Phones The basis of modern mobile phones
is the celular concept. Prior to this there were many radio telephones
u. . .goto page
0G Phones The basis of modern mobile phones
is the celular concept. Prior to this there were many radio telephones
u. . .goto pageGSM Reference Model - 2G
 GSM (Groupe Special Mobile) has published the underlying model and standards
for digital cellular communications; the. . .goto page
GSM (Groupe Special Mobile) has published the underlying model and standards
for digital cellular communications; the. . .goto pageBase Station Systems.

 In 2G the base station was made up of a Base Transceiver System and a Base
Station Controller. In 4G the same functio. . .goto page
In 2G the base station was made up of a Base Transceiver System and a Base
Station Controller. In 4G the same functio. . .goto pageCore Mobile Management

 At the edge of a mobile network is the base station or eNodeB or gNodeB. In
essence these systems manage the wireless . . .goto page
At the edge of a mobile network is the base station or eNodeB or gNodeB. In
essence these systems manage the wireless . . .goto pageHLR + AUC / HSS / UDM
 The Home Location Register (HLR) is the location in the 2G network where
various subscriber items are stored. This fun. . .goto page
The Home Location Register (HLR) is the location in the 2G network where
various subscriber items are stored. This fun. . .goto pageVisitors in a network
 The Visitor Location Register (VLR) allows roaming subscribers to use a
different network to their own network. For t. . .goto page
The Visitor Location Register (VLR) allows roaming subscribers to use a
different network to their own network. For t. . .goto pageEquipment Identity Register

 Each mobile network needs to keep lists of equipment that can and cannot
connect to their network. This is to ensure t. . .goto page
Each mobile network needs to keep lists of equipment that can and cannot
connect to their network. This is to ensure t. . .goto pageMobile Phone Masts
 A mobile phone mast is the interface between the wireless part of the network
and the base station, the backhaul netwo. . .goto page
A mobile phone mast is the interface between the wireless part of the network
and the base station, the backhaul netwo. . .goto pageMobile Network Coverage
 What a mobile phone customer requires is coverage for their phone on their
network at places they visit. To achieve th. . .goto page
What a mobile phone customer requires is coverage for their phone on their
network at places they visit. To achieve th. . .goto pageUser Equipment

 Talk of the mobile phone network and the obvious device that can connect to the
network is a mobile phone. But these a. . .goto page
Talk of the mobile phone network and the obvious device that can connect to the
network is a mobile phone. But these a. . .goto pageCellular Concept
 Some key factors in building a cellular network :
The network has to cope with large numbers of subscribers
. . .goto page
Some key factors in building a cellular network :
The network has to cope with large numbers of subscribers
. . .goto pageHandover
 Handover and handoff are different words for the same idea.
The basics of mobile phone technology is that when a cl. . .goto page
Handover and handoff are different words for the same idea.
The basics of mobile phone technology is that when a cl. . .goto pageRegistration and Roaming

 When a customer walks out of a shop with a new phone and new SIM, the shop staff
will have registered the SIM on their. . .goto page
When a customer walks out of a shop with a new phone and new SIM, the shop staff
will have registered the SIM on their. . .goto pageFrequencies for Mobile Communications
 In the UK OfCOM are responsible for the allocation and oversight of the
frequencies used for communications. This cove. . .goto page
In the UK OfCOM are responsible for the allocation and oversight of the
frequencies used for communications. This cove. . .goto pageMobile Phone Technology Basics
 When purchased, the SIM is registered by a network, the details are
stored in the home network (HLR or HSS) with. . .goto page
When purchased, the SIM is registered by a network, the details are
stored in the home network (HLR or HSS) with. . .goto pagePhone Numbers
 How do we identify the mobile device? - a phone number?
International Network Operator is the number that identifi. . .goto page
How do we identify the mobile device? - a phone number?
International Network Operator is the number that identifi. . .goto pageConverting Phone Calls to Digital.
 When we talk the sound waves are analogue sound waves but these need to be
converted to a stream of numbers, which can. . .goto page
When we talk the sound waves are analogue sound waves but these need to be
converted to a stream of numbers, which can. . .goto pageMobile Network Virtual Operators (UK)
 In addition to the MNOs in the UK there are a number of Mobile Virtual
Network Operators. These organisations sell mo. . .goto page
In addition to the MNOs in the UK there are a number of Mobile Virtual
Network Operators. These organisations sell mo. . .goto pageMultiplexing or Multiple Access

 There is a limited amount of bandwidth available to the mobile phone operators
which are split into channels. One of t. . .goto page
There is a limited amount of bandwidth available to the mobile phone operators
which are split into channels. One of t. . .goto pageModulation
 The data, in terms of 0's and 1's needs to be sent on a carrier
wave at a specific frequency. For example Vodafone use. . .goto page
The data, in terms of 0's and 1's needs to be sent on a carrier
wave at a specific frequency. For example Vodafone use. . .goto pageGeneric Mobile Reference Architecture
 The different generations of mobile phone technology are based on a similar
mobile network architecture. In order to h. . .goto page
The different generations of mobile phone technology are based on a similar
mobile network architecture. In order to h. . .goto pageGPRS networks
 GPRS, often called 2.5G, is a enhancement to the initial 2G network. The 2G
network was a phone network and data was . . .goto page
GPRS, often called 2.5G, is a enhancement to the initial 2G network. The 2G
network was a phone network and data was . . .goto page3G Mobile Network
 The 3G network built upon the architecture of the GPRS / 2.5G network.
The user equipment connected through the air in. . .goto page
The 3G network built upon the architecture of the GPRS / 2.5G network.
The user equipment connected through the air in. . .goto pageFramework for the 4G mobile Network.
 The move to 4G is a move to an Enhanced UTRAN architecture or an enhanced
3G network. The technology behind 4G is LTE. . .goto page
The move to 4G is a move to an Enhanced UTRAN architecture or an enhanced
3G network. The technology behind 4G is LTE. . .goto pageWAP
 The mobile Internet became available around 1999. The first phones, such as
the Nokia 7110, were monochrome, small me. . .goto page
The mobile Internet became available around 1999. The first phones, such as
the Nokia 7110, were monochrome, small me. . .goto pageMobile Web Overview
 From 1990 it has been possible to see web pages on a mobile, the Nokia 7110 being
one of the first devices. This was a. . .goto page
From 1990 it has been possible to see web pages on a mobile, the Nokia 7110 being
one of the first devices. This was a. . .goto pagenative Apps for Mobiles
 There are millions of applications available for the mobile phone owner to
download to their phone covering every conc. . .goto page
There are millions of applications available for the mobile phone owner to
download to their phone covering every conc. . .goto pageCell Splitting and Small Cells.

 The basics of cell splitting is to reduce the strength of the signal of an
antenna, this reducing the area of coverag. . .goto page
The basics of cell splitting is to reduce the strength of the signal of an
antenna, this reducing the area of coverag. . .goto pageSMS = Short Messaging Service


 SMS is the Short Messaging System available on all mobile phones. An app on a
user's phone will allow them to send an. . .goto page
SMS is the Short Messaging System available on all mobile phones. An app on a
user's phone will allow them to send an. . .goto pageMessaging Apps
 Every phone will
have an SMS App which is used to send SMS messages.
If the message is longer than the 160 c. . .goto page
Every phone will
have an SMS App which is used to send SMS messages.
If the message is longer than the 160 c. . .goto pageWAP Push Messages
 WAP Push is a special type of SMS message that is pushed to the recipient.
The data sent is one of two types :
. . .goto page
WAP Push is a special type of SMS message that is pushed to the recipient.
The data sent is one of two types :
. . .goto pageMMS Messages
 MMS is the Mulitmedia messages service available on all modern phones phones.
It is advertised as adding rich media s. . .goto page
MMS is the Mulitmedia messages service available on all modern phones phones.
It is advertised as adding rich media s. . .goto pageCell Sectorisation.
 The typical schematic for mobile coverage shows perfect hexagons with an
omnidirectional antenna at the centre. If dem. . .goto page
The typical schematic for mobile coverage shows perfect hexagons with an
omnidirectional antenna at the centre. If dem. . .goto pageEDGE networks
 EDGE = Enhanced Data-rates for GPRS Evolution
On a modern smartphone, users will see, in areas of 2G network coverage,. . .goto page
EDGE = Enhanced Data-rates for GPRS Evolution
On a modern smartphone, users will see, in areas of 2G network coverage,. . .goto page2G Wireless Phones.
 G initiated the move to digital technology from the original analogue technology.
This allows for greater network capac. . .goto page
G initiated the move to digital technology from the original analogue technology.
This allows for greater network capac. . .goto pageLong SMS Messages
 A standard SMS message will send messages of at most 160 7-bit characters
to a recipient. But what if the message to b. . .goto page
A standard SMS message will send messages of at most 160 7-bit characters
to a recipient. But what if the message to b. . .goto page4G-LTE Network
 3G-HSPA+ technology has squeezed a fast capable network from the 3G mobile
phone network. But there is still a demand . . .goto page
3G-HSPA+ technology has squeezed a fast capable network from the 3G mobile
phone network. But there is still a demand . . .goto pagePhase Modulation
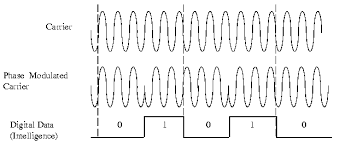 The basis of phase modulation is that changes are made to the phase of the
carrier wave and these changes represent 0 . . .goto page
The basis of phase modulation is that changes are made to the phase of the
carrier wave and these changes represent 0 . . .goto page3G Wireless Network
 G Edge had squeezed a lot out of an older network design but there was still a
demand for data. The main goal for the 3. . .goto page
G Edge had squeezed a lot out of an older network design but there was still a
demand for data. The main goal for the 3. . .goto pageFrequency Physics.
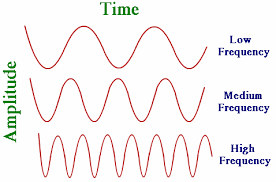 requencies used for mobile phone technology range from 800MHz to 3.8GHz; with
26GHz and 40GHz coming on stream.
Thes. . .goto page
requencies used for mobile phone technology range from 800MHz to 3.8GHz; with
26GHz and 40GHz coming on stream.
Thes. . .goto pageHSPA / HSPA+ networks
 HSPA - High Speed Packet Access
HSDPA - High Speed Download Packet Access
HSUPA - High Speed Upload Packet Acc. . .goto page
HSPA - High Speed Packet Access
HSDPA - High Speed Download Packet Access
HSUPA - High Speed Upload Packet Acc. . .goto pageOFDMA

 OFDM splits the spectrum into 15kHz sub-channels but allocates the whole channel
to a single user for the specified t. . .goto page
OFDM splits the spectrum into 15kHz sub-channels but allocates the whole channel
to a single user for the specified t. . .goto pageMIMO
 MIMO, is multiple input, multiple output meaning that the signals are transmitted
on different frequencies to differen. . .goto page
MIMO, is multiple input, multiple output meaning that the signals are transmitted
on different frequencies to differen. . .goto page4G+ Networks
 How to speed up 4G? The LTE Advance, often referred to as 4G+, is a technology
used to produce more speed out of the e. . .goto page
How to speed up 4G? The LTE Advance, often referred to as 4G+, is a technology
used to produce more speed out of the e. . .goto pageWiFi and Mobiles
 Wifi is a wireless communication technology designed to allow computing devices
to send data to and receive data from. . .goto page
Wifi is a wireless communication technology designed to allow computing devices
to send data to and receive data from. . .goto pageMobile Broadband

 There are two classes of mobile router as illustrated by the images. A 'mobile'
mobile router is one that can be carri. . .goto page
There are two classes of mobile router as illustrated by the images. A 'mobile'
mobile router is one that can be carri. . .goto pageApple iPhones

 In 2007 Apple released their first phone, the iPhone. A touch sensitive screen
rather than a keyboard and a large, for. . .goto page
In 2007 Apple released their first phone, the iPhone. A touch sensitive screen
rather than a keyboard and a large, for. . .goto pageSamsung Galaxy S Phones
 In 2010 Samsung released their Galaxy S range of phones as their flagship
phone. These phones have, over the years, d. . .goto page
In 2010 Samsung released their Galaxy S range of phones as their flagship
phone. These phones have, over the years, d. . .goto pageQAM - Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
 There is always a demand to deliver more bits on the carrier wave. 8PSK will
deliver 3 bits (8 values) but this me. . .goto page
There is always a demand to deliver more bits on the carrier wave. 8PSK will
deliver 3 bits (8 values) but this me. . .goto page4G-Drivers for the Technology
 Why is 3g not good enough? What are the technology drivers that will give the
demand for 4G technology. If there i. . .goto page
Why is 3g not good enough? What are the technology drivers that will give the
demand for 4G technology. If there i. . .goto page5G Drivers for the Technology
 A familiar question - why is 4G not good enough? 5G has 3 (potential) impovements
over the 4G network namely more c. . .goto page
A familiar question - why is 4G not good enough? 5G has 3 (potential) impovements
over the 4G network namely more c. . .goto page5G - Overview of Technology
 5G is the latest generation of mobile phone technologies, following on from 4G.
Indeed it is envisaged that 5G will wo. . .goto page
5G is the latest generation of mobile phone technologies, following on from 4G.
Indeed it is envisaged that 5G will wo. . .goto page5G Bandwidth Auction in UK
 5G will be delivered (in UK) using a mix of 3 spectrum bands :
700Mhz - to provide the coverage over large areas. . .goto page
5G will be delivered (in UK) using a mix of 3 spectrum bands :
700Mhz - to provide the coverage over large areas. . .goto pageVirtual SMS.
 Many companies use SMS messages to communicate with customers. For example :
Marketing or Advertising
Second of. . .goto page
Many companies use SMS messages to communicate with customers. For example :
Marketing or Advertising
Second of. . .goto pageFormat of SMS messages.
 n SMS message is sent as a series of 140 8 bit characters. These can be decoded
into 160 7 bit characters (as usual in. . .goto page
n SMS message is sent as a series of 140 8 bit characters. These can be decoded
into 160 7 bit characters (as usual in. . .goto pageRCS Messaging
 SMS is the most basic of mobile messaging systems.
There have been enhancements to allow long messages
(over 160 c. . .goto page
SMS is the most basic of mobile messaging systems.
There have been enhancements to allow long messages
(over 160 c. . .goto pageLTE for Machines (LTE-M)

 The model for IoT or Smart devices is that these can be located anywhere but
they need some element of communication t. . .goto page
The model for IoT or Smart devices is that these can be located anywhere but
they need some element of communication t. . .goto pageCarrier Aggregation

 In a 4G-LTE environment the available bandwidth is split into channels, or
component carriers. The standard sizes of . . .goto page
In a 4G-LTE environment the available bandwidth is split into channels, or
component carriers. The standard sizes of . . .goto pageNetwork Slicing
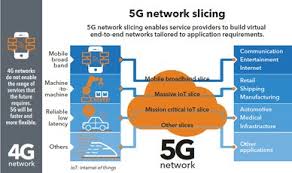 In a 4G network each operator will run a general purpose network supporting the
range of use, from browsing the Inter. . .goto page
In a 4G network each operator will run a general purpose network supporting the
range of use, from browsing the Inter. . .goto pageHeath Issues of Mobile Technology
 With every new generation of mobile phone technology there are claims that the
radiation associated with the technolog. . .goto page
With every new generation of mobile phone technology there are claims that the
radiation associated with the technolog. . .goto page5G Small and Macro cells.
 The big change implemented in 5g is (will be) mmWave, transmission frequency at 26GHz.
These waves have a large capac. . .goto page
The big change implemented in 5g is (will be) mmWave, transmission frequency at 26GHz.
These waves have a large capac. . .goto pageVoLTE
 VoLTE - Voice over LTE - is the protocol for using the 4G network for phone calls.
2G and 3G networks wer. . .goto page
VoLTE - Voice over LTE - is the protocol for using the 4G network for phone calls.
2G and 3G networks wer. . .goto pageSDL
 In a normal mobile connection the channel used is a pair of channels, one
uplink and one downlink. The mo. . .goto page
In a normal mobile connection the channel used is a pair of channels, one
uplink and one downlink. The mo. . .goto pageCGNAT- Carrier Grade Network Address Translation
 When your phone is connected to the mobile network it needs an IP address so
that your phone can be found.There are t. . .goto page
When your phone is connected to the mobile network it needs an IP address so
that your phone can be found.There are t. . .goto pageOFDM
 Orthogonal Freequency Division Multiplexing is a mixture of frequency multiplexing,
spliiting the available frequency. . .goto page
Orthogonal Freequency Division Multiplexing is a mixture of frequency multiplexing,
spliiting the available frequency. . .goto pageBeam Forming
 Most mobile masts, in busy areas, are arranged to receive and send data within
a 120 degree sector. These masts will . . .goto page
Most mobile masts, in busy areas, are arranged to receive and send data within
a 120 degree sector. These masts will . . .goto page5G - NR vs SA
 5G in UK - the 4 mobile operators, EE, O2, 3UK and
Vodafone each bought frequencies to be able to run a 5G network. T. . .goto page
5G in UK - the 4 mobile operators, EE, O2, 3UK and
Vodafone each bought frequencies to be able to run a 5G network. T. . .goto pagePhones that changed our lives 1
 Nokia 7110 (2000)
The Nokia 7110 was a notable phone as it was at the start of the data revolution.
Prior to . . .goto page
Nokia 7110 (2000)
The Nokia 7110 was a notable phone as it was at the start of the data revolution.
Prior to . . .goto pagePhones that changed our lives 3
 Nokia N95 (2007)
The N95 was the flagship Noki phone which were released to deliver 3G. This phone
had a much. . .goto page
Nokia N95 (2007)
The N95 was the flagship Noki phone which were released to deliver 3G. This phone
had a much. . .goto pagePhones that changed our lives 2
 Nokia 6230 (2003)
The Nokia 6230 was significant because of the (small) colour screen. Also it
supported HTML. . .goto page
Nokia 6230 (2003)
The Nokia 6230 was significant because of the (small) colour screen. Also it
supported HTML. . .goto pageVoIP
 VoIP is the making of a phone call over the Internet.
Making phone calls over the Internet has been the 'norm' for . . .goto page
VoIP is the making of a phone call over the Internet.
Making phone calls over the Internet has been the 'norm' for . . .goto pageVo-WiFi - Voice over WiFi
 If your phone is connected to a WiFi network and you wish to make or receive a
call then this can be carried out seam. . .goto page
If your phone is connected to a WiFi network and you wish to make or receive a
call then this can be carried out seam. . .goto pageFramework for the 5G mobile Network.
 There are 2 variants of 5G in the Uk; 5G-SA (Stand Alone) and 5G-NR (New Radio).
In the case of 5G-NR this is the 5G r. . .goto page
There are 2 variants of 5G in the Uk; 5G-SA (Stand Alone) and 5G-NR (New Radio).
In the case of 5G-NR this is the 5G r. . .goto pageFDD and TDD.
 The channel used to transmit data in 2G, 4G and 5G needs to be shared between
users. This sharing is done by either s. . .goto page
The channel used to transmit data in 2G, 4G and 5G needs to be shared between
users. This sharing is done by either s. . .goto pagee-SIM.
 A SIM card is a Subscriber Identity Module, and is the way the network
identifies the device on the network. It . . .goto page
A SIM card is a Subscriber Identity Module, and is the way the network
identifies the device on the network. It . . .goto page© mobilephonetechnology.co.uk all rights reserved 2017-2025
