Generic Mobile Reference Architecture
A Generic Framework for Mobile Communications.
© copyright fromgenttogen.us
2G Networks
2.5G Networks
3G Networks
4G Networks
5G Networks
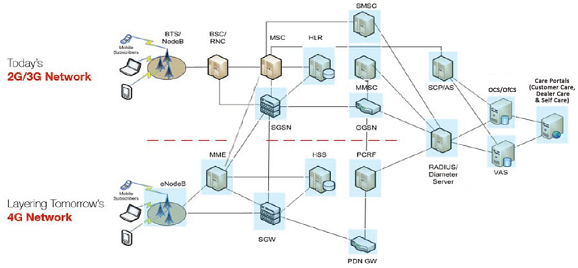
The different generations of mobile phone technology are based on a similar mobile network architecture. In order to help the understanding of the architecture of 2G, 3G and 4G networks; a generic mobile reference architecture is presented here. There are a number of different nomenclature for essentially the same thing running through these architectures. This model is an attempt to help compare the architectures for these different names and models.
Overall there are 4 different aspects to the Generic Mobile Architecture :
- Mobile device. This is the device that the user uses to connect to the network. Often though of as the moble phone but other devices can connect to the mobile network.
- Wireless Network Through this wireless network, the Mobile Device connects to a mast or ground station.
- Base Station which is the receiving mast and transceiver plus the controller(s) to manage this function
- The next is the Core Network that takes the communications from the Base Station and processes these to send out to the trunk networks within the country be that PDSN or IP Based.
- Operational Support is the fourth element within the architecture and whilst it does not contribute to the data transfer it is essential for management of the network in the widest sense.
The table below gives an overview of the different components in 2G + 2.5G / 3G / 4G networks.
| 2G | 2.5G | 3G | 4G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User equipment | Mobile Station + SIM | Mobile Station + SIM | User Equipment + USIM | LTE User Equipment + LTE-USIM |
| Wireless Communications | 900 / 1800 MHz TDMA | 900 / 1800 MHz TDMA | 2.1GHz CDMA | 800 / 2.6GHz CDMA |
| Base Station | Base Station Subsystem BTS / BSC | Base Station Subsystem BTS / BSC | Node B RNC | eNode B MME |
| Operational Support | OMC VLR HLR AUC EIR | OMC VLR HLR AUC EIR | OMC VLR HLR AUC EIR | MME HSS |
| Core Network | Mobile Switching Centre | GPRS Switching Node = Serving GPRS Support Node and Gateway GSN | Serving GPRS Support Node and Gateway GSN | Serving Gateway an Packet Gateway |
| Trunk Network | PSTN | IP | IP | IP |
*u* ©mobilephonetechnology.co.uk all rights reserved 2017- 2025



